BIM for Quantity Surveyors (QS) is a digital process that transforms traditional cost estimation and quantity take-off by using intelligent 3D models filled with data. The technology allows quantity surveyors to extract accurate measurements directly from the digital model, saving time and minimizing manual errors. Cost estimation becomes more precise, and real-time updates ensure that every design change is reflected in project costs immediately. As a result, BIM improves collaboration among project teams and enhances cost management from early feasibility studies through the final account stage.
This article provides an overview of how BIM is shaping the future of quantity surveying and why it is becoming an essential skill for modern QS professionals. The following sections will examine how BIM enhances accuracy, fosters coordination, and facilitates sustainable decision-making in cost planning. By understanding these benefits, quantity surveyors can adopt BIM effectively and contribute to smarter, data-driven project delivery.
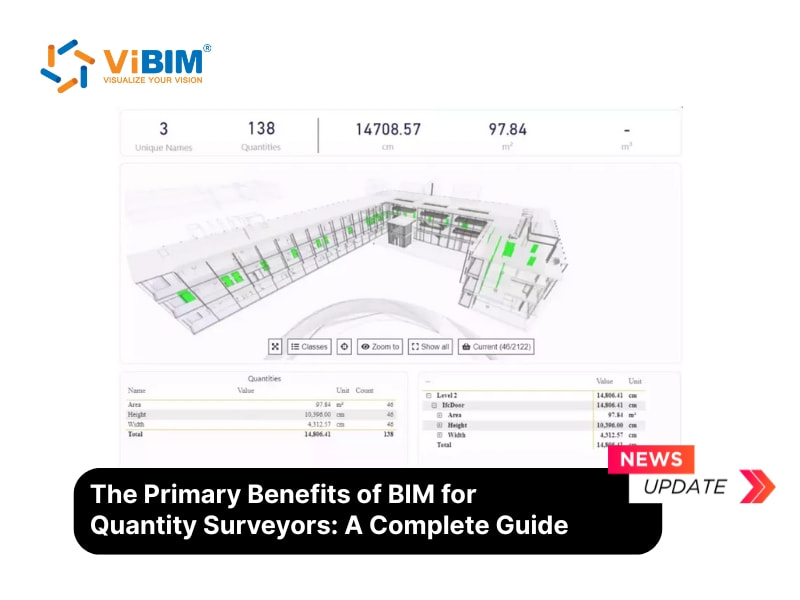
How can a quantity surveyor use BIM?
A Quantity Surveyor’s role is critical in managing construction costs effectively. BIM provides powerful tools to augment and streamline these responsibilities. Instead of manually measuring drawings or dealing with fragmented information, a QS can leverage the data-rich BIM model. There are four main ways a quantity surveyor can use BIM as part of their role:
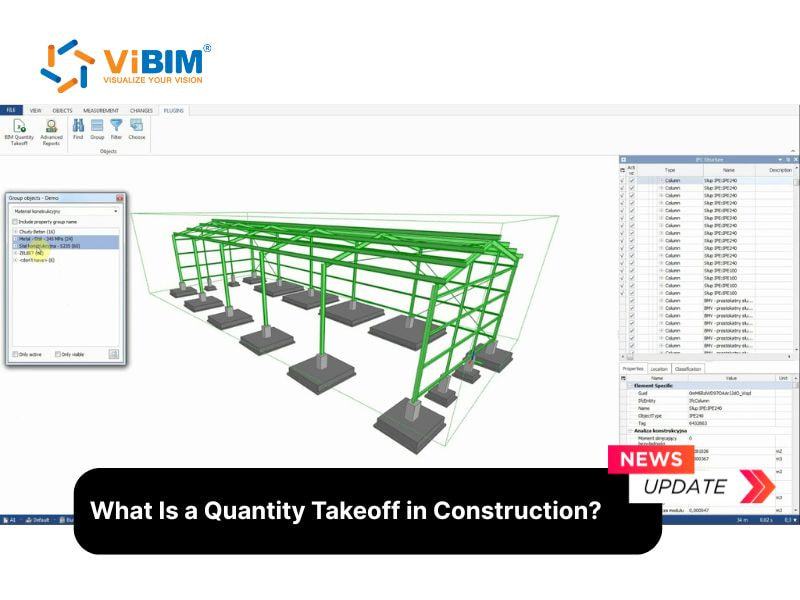
- Automatic creation of quantity takeoff, where each element in the 3D model carries detailed information about materials and dimensions, often requiring precise family creation in Revit to ensure data reliability.
- Creation of 3D models that help interpret complex project layouts and design relationships more accurately.
- Execution of clash detection to identify design conflicts early and prevent costly rework during construction.
- Management of project costs by linking quantity and price data directly to the BIM model, updating all information simultaneously as designs change.
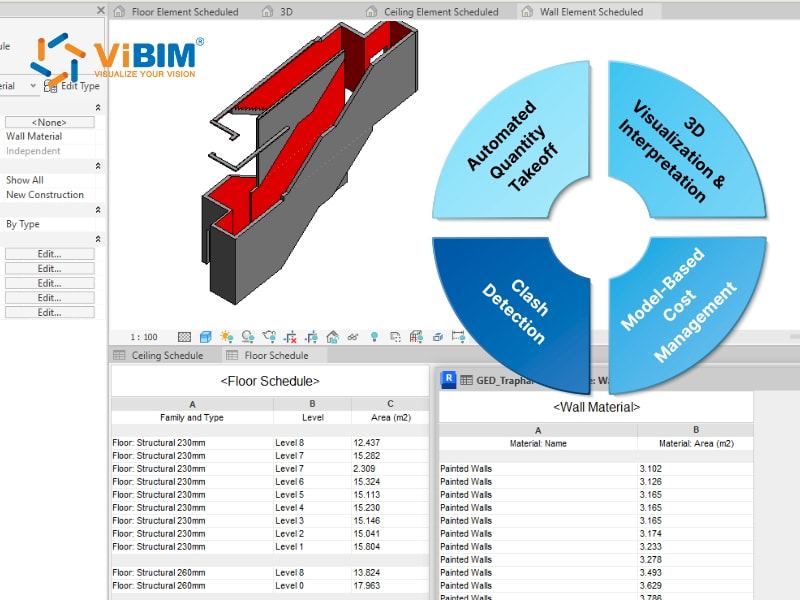
BIM usage by quantity surveyors
Global adoption of BIM has grown rapidly across industries as professionals recognize its value for project efficiency and data accuracy. Different countries have shown varying adoption rates, reflecting the evolution of BIM maturity driven by government policies, industry readiness, and technology investment.
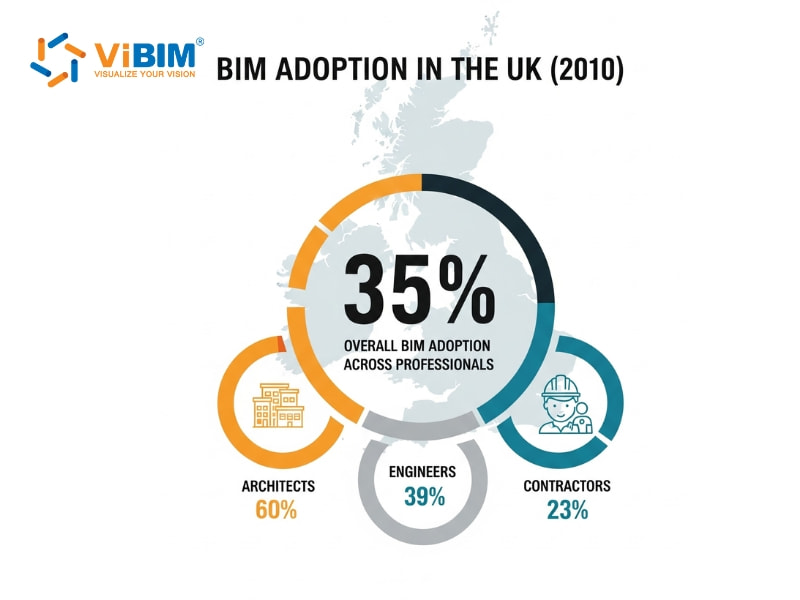
- In the UK (2010), BIM adoption reached 35% across professionals, with 60% among architects, 39% among engineers, and 23% among contractors.
- In New Zealand, awareness and usage increased from 34% in 2011 to 57% in 2012, while non-users dropped sharply from 12% to 2%.
- In South Korea, 92% of BIM users reported visible project benefits and positive returns on investment.
According to a Royal Institution of Chartered Surveyors (RICS) survey in 2011, around 10% of 156 quantity surveyors regularly used BIM, mainly during the design and construction stages. Their key applications involved scheduling, quantity extraction, and asset management, laying the groundwork for future BIM for facility management integration. Another 10% were actively testing BIM software for future use. The major obstacles to wider adoption included low client demand, lack of training, incompatible software, and limited standardization.
What are the benefits of BIM for quantity surveyors?
The following are the 7 primary benefits of implementing BIM for quantity surveyor:
- Enhanced accuracy and efficiency in cost estimation
- Improved visualization and understanding (Data visualization)
- Enhanced collaboration and data coordination
- Better cost control and risk management
- Faster Tendering and Procurement
- Enhanced Professional Role
In this part, we will examine each of these benefits in greater detail to understand how they strengthen cost planning and project performance.
Enhanced accuracy and efficiency in cost estimation
Traditional cost estimation relied on interpreting 2D drawings, a process often prone to human error, missing details, and time-consuming manual measurements. Quantity surveyors had to manually calculate quantities, compare revisions, and update spreadsheets, which made it difficult to maintain consistent accuracy and real-time cost control throughout the project.
BIM transforms this process by creating intelligent 3D models that integrate all geometric, material, and specification data into a single, unified platform. These models provide precise digital information that can be automatically extracted for take-offs, significantly reducing manual effort and minimizing the risk of misinterpretation. According to a study by Z. Shen and R. R. A. Issa (2010), automated calculations using BIM reduced estimating time by around 46% for complex cases and achieved cost deviations of less than 5% in 87% of estimates, compared to only 40% for manual methods.
With 5D BIM, cost and timeline data are integrated directly into the 3D model, enabling quantity surveyors to analyze financial impacts in real-time as design changes occur. This integration links materials, labor, and equipment costs to project schedules, enabling earlier and more accurate forecasting. By maintaining live connections between design, cost, and time, quantity surveyors can track how every design decision affects the overall budget and project duration.
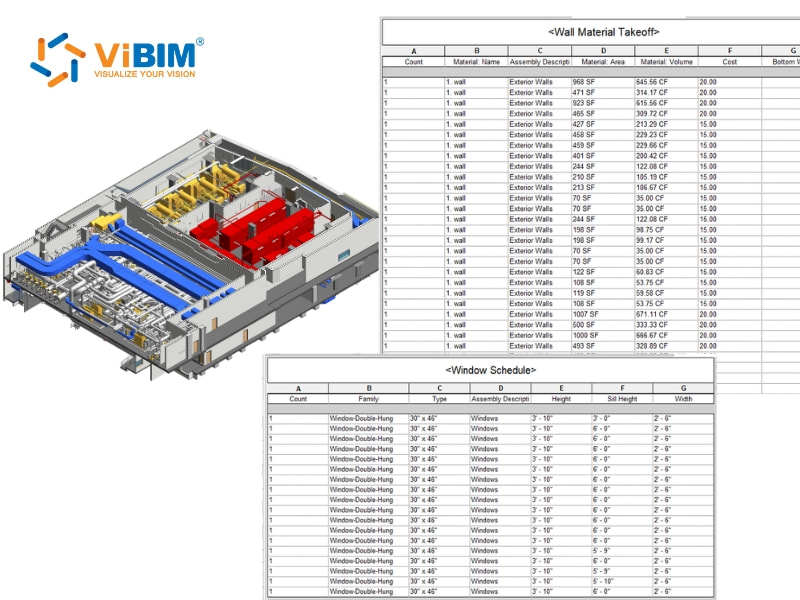
Improved visualization and understanding (Data visualization)
Quantity surveying depends on a clear understanding of every project detail. Traditional 2D drawings often limit surveyors’ ability to interpret spatial relationships and design intent, leading to misinterpretations and missed conflicts. BIM addresses this limitation by creating intelligent 3D models that enable quantity surveyors to visualize how materials, systems, and structures interconnect in real-world space.
By visualizing the project in 3D, quantity surveyors can identify potential design issues before construction begins, reducing costly rework and minimizing risks. Research by P. Rajendran, T. Seow, and K. Goh (2013) found that multi-angle visual review in BIM enhances early conflict detection accuracy, enabling teams to resolve issues long before they appear on-site.
BIM’s visual environment also strengthens communication across disciplines. Complex project data becomes easier to interpret and discuss, enabling both technical and non-technical stakeholders to understand project status and potential risks. Research by C. Furneaux and R. Kivvits (2008) highlights that visual representation in BIM accelerates decision-making and improves collaboration, ensuring that every team member works from a shared understanding.
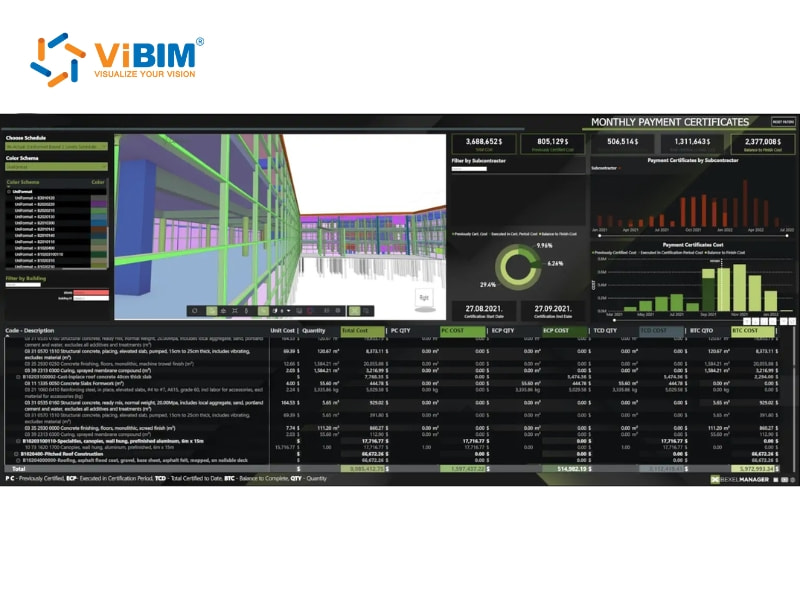
Enhanced collaboration and data coordination
BIM creates a shared digital environment where all project participants work with the same up-to-date information. By centralizing models, drawings, schedules, and quantities in a single system, BIM ensures that everyone, from architects to quantity surveyors, has access to consistent and reliable data. This shared foundation eliminates duplication, reduces discrepancies between disciplines, and ensures seamless BIM coordination, allowing teams to collaborate more effectively throughout the project lifecycle.
An integrated model also supports real-time updates and feedback, helping teams respond quickly to design changes. Quantity surveyors can review cost implications while designers refine details, enabling proactive decision-making rather than reactive adjustments. According to Logan, Jackson, and Hainsworth (Aurecon), BIM’s strength lies in connecting and interpreting information as an intelligent model, thereby promoting collaboration and aligning team efforts within a unified workflow.
Shared access also improves accountability and transparency. Every model edit, comment, or approval is recorded by author and time, creating a clear audit trail that builds trust among stakeholders. This transparent communication ensures that all participants remain aligned, informed, and responsible for maintaining project quality and efficiency.

Better cost control and risk management
BIM empowers quantity surveyors to manage project costs and risks with higher accuracy and foresight. By integrating real-time data, BIM analytics, and simulation tools, BIM transforms cost control into a proactive process that anticipates financial risks before they occur. This data-driven approach helps surveyors not only track expenses but also predict potential overruns and optimize resource allocation throughout the project lifecycle.
With integrated cost data, quantity surveyors can perform scenario-based simulations to test different design and material options. These “what-if” analyses visualize the financial impact of each change in real time, supporting value-driven decisions. Research by P. Smith (2014) demonstrates that 5D BIM integration facilitates continuous value management and budget control, enabling cost managers to maintain accurate, up-to-date cost plans throughout the design and construction phases.
By combining design, schedule, and cost data into a single model, BIM enables comprehensive risk management. Quantity surveyors can anticipate challenges such as material shortages, sequencing conflicts, or budget deviations and adjust strategies before they impact the project. This integrated visibility supports smarter financial planning and contributes to more stable and predictable project outcomes.
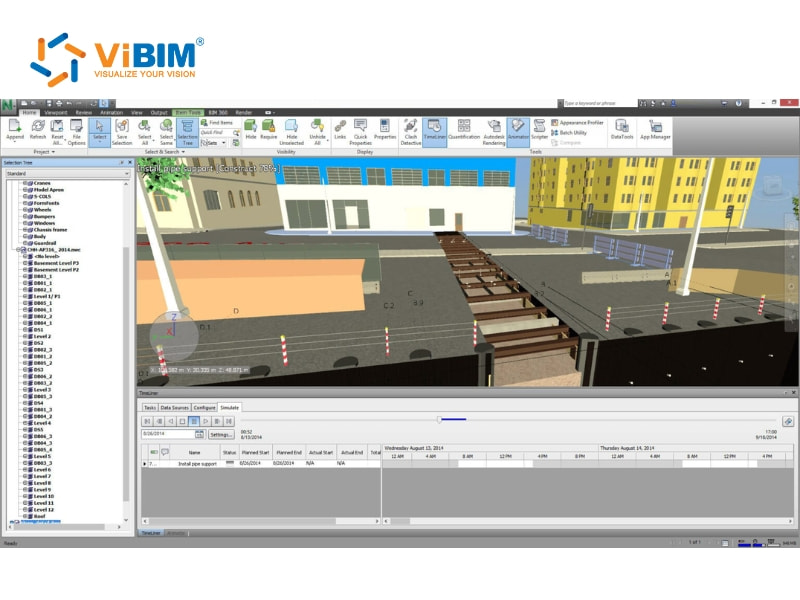
Faster Tendering and Procurement
The accuracy of the BIM model streamlines the tendering and procurement process. Because the model provides accurate quantities for most materials and objects, these figures can be used to procure materials from vendors and subcontractors with greater confidence.
Furthermore, the ability to visualize the construction process (4D BIM) helps in planning the schedule and logistics, ensuring just-in-time arrival of materials and reducing on-site inventory costs. This efficiency reduces the production cycle times and allows for more competitive and accurate tendering.
Enhanced Professional Role
Instead of spending 70–80 % of time on repetitive measurement, QS can focus on higher-value tasks: cost planning, value engineering, risk management, sustainability costing, and strategic advice.
Rather than being seen merely as “counters,” QS professionals using BIM become integral data managers who contribute to the project’s profitability and efficiency. This shift requires new skills but ultimately places the QS at the center of the digital construction workflow.
Challenges in using BIM for quantity surveying
While BIM offers clear advantages for enhancing project efficiency and accuracy, it also presents five challenges that must be addressed for quantity surveyors to fully leverage its capabilities. These challenges include technical limitations, skill shortages, and cost barriers that can slow adoption and reduce its effectiveness.
- Technical and integration limitations: BIM implementation requires an upgraded digital infrastructure capable of handling high data volumes while remaining compatible with other software platforms. Limited interoperability often leads to data duplication or loss during model exchange and cost estimation, thereby affecting consistency and reliability in project reporting.
- Resistance to change and human factors: Adopting new digital workflows can be difficult when professionals are more comfortable with traditional 2D methods. Fear of technology, lack of leadership support, and limited time for training all contribute to slower adoption, making organizational change management a key challenge.
- Lack of standardized processes and protocols:Different stakeholders often apply BIM practices inconsistently, frequently due to the lack of a defined BIM execution plan, leading to data mismatches and coordination gaps. The lack of unified industry standards impedes seamless collaboration and hinders the exchange of accurate cost information across teams and project phases.
- Skill and training gaps among quantity surveyors: BIM requires advanced digital skills such as 3D modeling, data analysis, and integrated cost control, which are often beyond traditional QS training. Without continuous education and structured training programs, many professionals struggle to apply BIM effectively in practice.
- High initial and ongoing costs: Investing in BIM software, hardware upgrades, and staff training demands a large financial commitment. Recurring expenses for updates, technical support, and license renewals can further strain resources, especially for smaller organizations operating on limited budgets.
To ensure your organization navigates these hurdles successfully and maximizes its investment, learn how to avoid the most common mistakes in BIM implementation.
A Quantity Surveyor’s Breakdown: Comparing Quantity Takeoff Methods in BIM Software
The software you use for quantity takeoff defines the entire workflow. Across the major solutions, the methods for pulling data fit into four main categories. Here is a breakdown of their different approaches.
- Model-Based Native Extraction: This method extracts schedules directly from the native modeling software, like Revit or Tekla. Quantity surveyors often use this for its direct, reliable data link.
- BIM Viewer & Aggregator: These tools, such as Navisworks or Assemble, federate different BIM files. The platform then reads the object information from all combined models to aggregate a schedule, though this path is used less frequently.
- Hybrid 2D/3D Solutions: Specialized QTO software like CostX or Autodesk Takeoff dominates this category. These platforms process data from imported BIM models and allow manual input from 2D drawings, making them highly practical and very common today.
- 2D-Focused Traditional: Tools like Bluebeam remain very popular in many regions. Users import 2D files, like PDFs, and then manually trace measurements or assign properties, which the software then compiles into a final quantity.
But let’s be honest, real-world quantity takeoff is messy. It’s rare to use just one of these methods. A “pure BIM” workflow often isn’t possible because the input files a quantity surveyor receives just aren’t “BIM-standard.” This reality means that the hybrid approach, which blends 3D model data with 2D verification, remains the most common and necessary strategy in the field.

How do ViBIM’s services help quantity surveyors?
ViBIM’s Scan to BIM services provide quantity surveyors with highly accurate 3D as-built models that convert complex site data into reliable, usable project information. Each model is developed from high-quality point cloud data, ensuring precision in material planning, quantity takeoffs, and cost estimation. This accuracy helps minimize errors commonly found in traditional measurement processes, supporting better budget control throughout the project.
ViBIM specializes in BIM modeling services utilizing point cloud data, with Autodesk Revit as the primary authoring tool. Our solutions are designed to support building surveyors, renovation projects, and engineering teams by delivering data-driven, detailed as-built models. For firms lacking in-house capacity, we offer specialized Revit model outsourcing services to ensure reliable existing-condition data essential for accurate cost and quantity assessments.
Contact ViBIM today to learn more about our Revit modeling services and receive a complimentary consultation for your project needs.
Vietnam BIM Consultancy and Technology Application Company Limited (ViBIM)
- Address: 10th floor, CIT Building, No 6, Alley 15, Duy Tan street, Cau Giay ward, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Phone: +84 944 798 298
- Email: info@vibim.com.vn
The article outlines the main benefits of BIM for quantity surveyors, explaining how accuracy, collaboration, data visualization, and sustainability contribute to more effective cost management. Each section aimed to clarify how BIM supports better project outcomes by simplifying data interpretation and improving coordination across teams.