BIM dimensions refer to the different levels of information and data layered into a Building Information Model for a particular use. Each dimension adds a specific type of data to the 3D model, transforming it from a simple geometric representation into a comprehensive digital database that supports a project’s entire lifecycle.
This guide provides a detailed breakdown of each BIM dimension, from the foundational 3D model through 4D (time), 5D (cost), 6D (sustainability), 7D (facility management), and 8D (safety), explaining the specific data and benefits associated with each.

What are BIM dimensions?
In the context of BIM, BIM dimensions refers to the different uses for a BIM process according to project stage requirement and project complexity. Each dimension is specific parameters or datasets that are integrated into a building information model for pre-defined specific purposes.
The purpose of BIM dimensions is to create a single source of truth that evolves with the project, providing the right information to the right people at the right time. For example, 3D represents physical space, 4D adds the element of time, and 5D incorporates cost. By adding these layers, stakeholders can simulate, analyze, and manage the project with greater accuracy and foresight than traditional methods allow.

Seven Types of BIM Dimensions
The industry has widely adopted a set of core dimensions that form the foundation of most BIM-enabled projects. These dimensions have their unique purpose and benefits, providing a holistic view of the building’s physical characteristics, schedule, cost, sustainability, and operational lifecycle, which are key components of the overall benefits of bim. In this section, we will explore different BIM dimensions, namely 2D, 3D, 4D, 5D, 6D, 7D, and 8D BIM dimensions.
2D BIM dimension
Before the advent of intelligent 3D modeling, 2D BIM represented the initial step into digital construction. A 2D BIM is a digital geometric model based on X and Y axes, typically created using CAD software. These early CAD systems were a significant leap forward, allowing plans and sections to be developed on computers more quickly and accurately than with manual, paper-based processes.
While most industry professionals no longer consider 2D geometry as true BIM today, it still provides the foundational parameters, constraints, and concepts associated with a model.

3D BIM dimension
3D is the most common use of BIM, representing the three geographical dimensions (x, y, z) of a building structure. The primary focus of 3D BIM is the creation of a detailed 3D BIM model and the sharing of this information among all project team members, often through a common data environment (CDE).
Benefits of 3D BIM dimension:
- Enhanced 3D visualization for clearer understanding of design intent.
- Streamlined communication and coordination among disciplines.
- Easy collaboration, reducing conflicts and rework.
- Early discovery of design errors and omissions before they become costly field issues
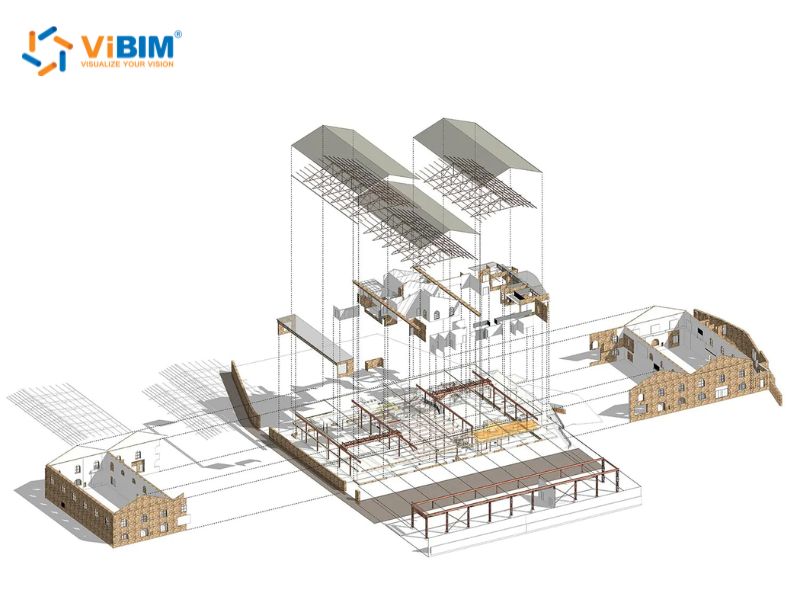
4D BIM dimension
The 4D dimension adds the crucial parameter of time to the 3D model, creating a powerful planning tool. The relationship can be summarized with a simple formula: 4D BIM = 3D BIM + Schedule. This process is often referred to as construction sequencing, as it involves linking scheduling data from project management tools, like Gantt charts, directly to the components in the 3D model.
This integration creates a dynamic visual simulation of how the project will be constructed and evolve over its timeline. Stakeholders can watch a virtual representation of the construction process, seeing exactly when and how different components will be installed. For project managers, this is an invaluable tool for spotting scheduling issues, overlaps between trades, and potential logistical problems long before they occur on-site. It allows teams to run various testing scenarios to see how the project would look at different phases of its realization, bridging the gap between visualization and reality.
Benefits of 4D BIM dimension:
- Improved site planning and logistics management.
- Seamless coordination of trades and material deliveries.
- Enhanced on-site safety by identifying potential sequencing hazards.
- Avoidance of costly delays through better schedule visualization and management.
5D BIM dimension
The 5th dimension of BIM integrates cost data directly into the model. This is useful in cases where budget analysis and cost estimation are required from the beginning of any project. As the design evolves, the 5D BIM model automatically updates quantity takeoffs and cost calculations, providing stakeholders with a clear view of the financial implications of any changes in scope, materials, or equipment.
For professionals looking to understand the technical side of this, exploring what is quantity take off is essential to mastering 5D workflows.
Benefits of 5D BIM dimension:
- Real-time cost visualization and accurate budget forecasting.
- Automatic and precise quantity takeoffs for materials and components.
- Simplified cost analysis of different design options.
- Minimization of budgetary overruns through continuous tracking.
Furthermore, the benefits of BIM for quantity surveyors are significant, as it allows for faster valuations and more accurate cost monitoring throughout the build.

6D BIM dimension
The 6D dimension focuses on sustainability and lifecycle information. It allows teams to analyze a building’s energy consumption and performance during the initial design stages, enabling informed decisions that reduce its environmental impact. Often called iBIM or integrated BIM, 6D also supports facility management by embedding key operational data—such as manufacturer details, maintenance schedules, and energy requirements—directly into the model components.
Benefits:
- Reduced lifelong energy consumption of the building.
- Faster, data-driven decision-making on sustainable components.
- Better operational management and cost control post-handover.
7D BIM dimension
The 7D dimension is dedicated to operations and facility management (FM) for the building’s entire lifecycle, a crucial niche for managers and owners. It consolidates all critical asset data—including technical specifications, manuals, warranty information, and required maintenance tasks—into a single, easily accessible location within the as-built model. Utilizing BIM for facility management ensures that this information is vital for ensuring the building operates efficiently from handover until its eventual demolition.
This approach collates all critical information related to the facility management process into a single, easily accessible location. It provides facility managers with a powerful tool for proactive management. For example, they can click on any component in the model, like an air handling unit, and instantly retrieve its maintenance history, warranty expiration date, and operating manual. This makes planning repairs, ordering parts, and scheduling maintenance incredibly efficient.
Benefits:
- Optimized asset and facility management from day one.
- Simplified and more efficient component replacements and repairs.
- Streamlined maintenance processes with readily available information.
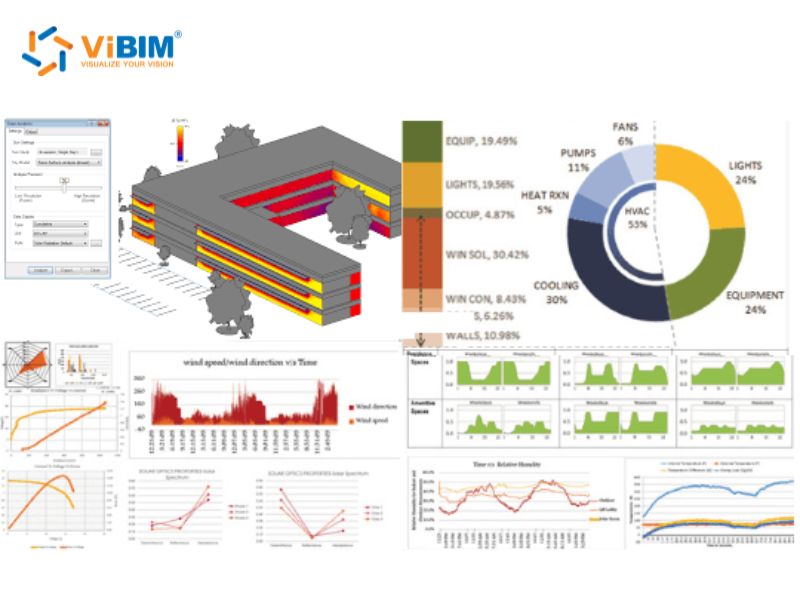
8D BIM dimension
The most widely accepted interpretation of 8D BIM is its focus on health and safety. This dimension uses the wealth of information that a BIM model has to predict and analyze every potential problem or accident that could result in human injury, directly addressing the construction industry’s long-standing challenges with on-site accidents.
Furthermore, the 8D model can be used with technologies like Virtual Reality (VR) to provide highly effective and immersive safety training for workers, preparing them for site-specific conditions in a controlled environment.

Other BIM Dimensions
Here are some of the most common use cases discussed:
9D BIM Dimension: Focus on Lean Construction
9D BIM is most commonly associated with Lean Construction principles. Its goal is to optimize every stage of the construction process to eliminate waste, reduce costs, and improve workflow efficiency. By using the data-rich BIM model, teams can analyze workflows, identify bottlenecks, and streamline activities to deliver maximum value to the owner.
10D BIM Dimension: Construction Industrialization
The 10D BIM dimension represents the future of construction: industrialization. This involves leveraging off-site construction, prefabrication, and modularization to improve quality, speed, and efficiency. BIM is the core enabler of this process, providing the highly detailed and accurate digital models needed to manufacture building components in a controlled factory environment for precise assembly on-site.
BIM Dimensions vs. Level of Development (LOD)
It is important to distinguish between BIM Dimensions and the Level of Development (LOD). While they are related, they refer to different aspects of a BIM model. To fully grasp this difference, it’s essential to understand what is BIM lod and how it defines the reliability of model elements.
- BIM Dimensions define WHAT type of information is in the model (e.g., time, cost, sustainability data).
- LOD defines HOW MUCH detail and reliability that information has.
To make this distinction perfectly clear, here is a direct comparison of the most prominent elements:
| Feature | BIM Dimensions | Level of Development (LOD) |
| Core Concept | Refers to the type of data layered onto the 3D model. | Refers to the degree of detail and reliability of the model elements. |
| Primary Question | “WHAT information are we adding?” | “HOW MUCH do we know about this element?” |
| Purpose | To enrich the model for specific types of analysis like scheduling (4D), cost estimation (5D), or facility management (7D). | To define the maturity and reliability of the model at different project stages, ensuring clarity for all stakeholders. |
| Analogy | Think of them as different lenses to view the project through (a time lens, a cost lens, a safety lens). | Think of it as the resolution of a picture. A low-res image (LOD 100) is conceptual, while a high-res image (LOD 400) is detailed. |
| Example | Adding a construction schedule to the 3D model creates 4D BIM. Adding cost data creates 5D BIM. | A wall is modeled as a generic mass (LOD 200). Later, it is defined with specific materials, layers, and rebar (LOD 350). |
| Focus | Focus is on functionality and what kind of analysis is possible. | Focus is on geometry, data reliability, and the suitability of the model for specific uses (e.g., cost estimation, fabrication). |
As a project matures from conceptual design (LOD 100) to design development (LOD 200) and construction documentation (LOD 300), the data within each BIM dimension becomes progressively more detailed. For instance, a 5D cost estimate at LOD 100 might be a rough, area-based calculation, whereas at LOD 300, it would be a detailed estimate based on specific, manufacturer-defined components. The dimensions enhance the model at each LOD stage, sharing a greater level of understanding and enabling more precise analysis as the project moves toward completion.
Clearly defining both the required BIM dimensions and the expected LOD at each project phase prevents misunderstandings, ensures the model is fit for its intended purpose, and aligns expectations among the architect, engineers, contractor, and owner.
Ultimately, understanding the full spectrum of BIM dimensions—from 2D drawings and 3D models to the advanced data layers of 4D time, 5D cost, and beyond—transforms a construction model into an intelligent lifecycle asset. This multi-dimensional approach empowers project teams to achieve crystal-clear visualization, optimize scheduling and cost management, integrate sustainability goals, and streamline long-term facility management. As the construction industry continues its digital transformation, a deep understanding of these dimensions is essential for delivering successful, high-quality projects with fewer resources and lower risk.
Transform these dimensions from theory to reality. At ViBIM, our expert 3D Revit BIM modeling services build the accurate, intelligent foundation your project needs to unlock its full potential.