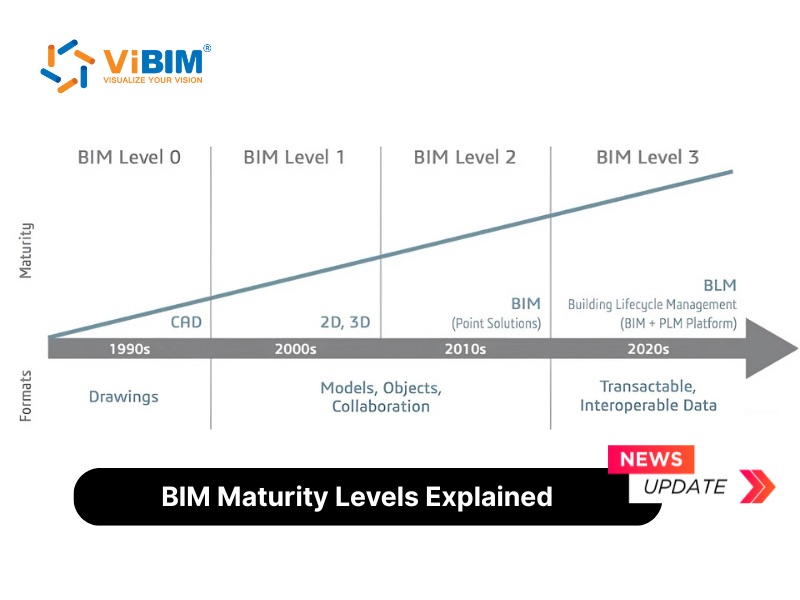
In the ever-evolving landscape of the Architecture, Engineering, and Construction (AEC) industry, projects are growing increasingly complex, and traditional 2D-based, fragmented communication methods often lead to inefficiencies and costly delays. Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers a transformative, collaborative approach to managing project data, allowing teams that adopt it early to achieve significant benefits throughout the project lifecycle. One of the most powerful extensions of this methodology is 4D BIM, which integrates the critical dimension of time by linking schedule data to the 3D model. This creates a dynamic, data-rich tool for virtual construction that provides a solution for better planning and management.
This article will define 4D BIM for construction, detail its substantial benefits, address potential implementation challenges, and examine its real-world applications and future role in shaping a more efficient and predictable construction industry.
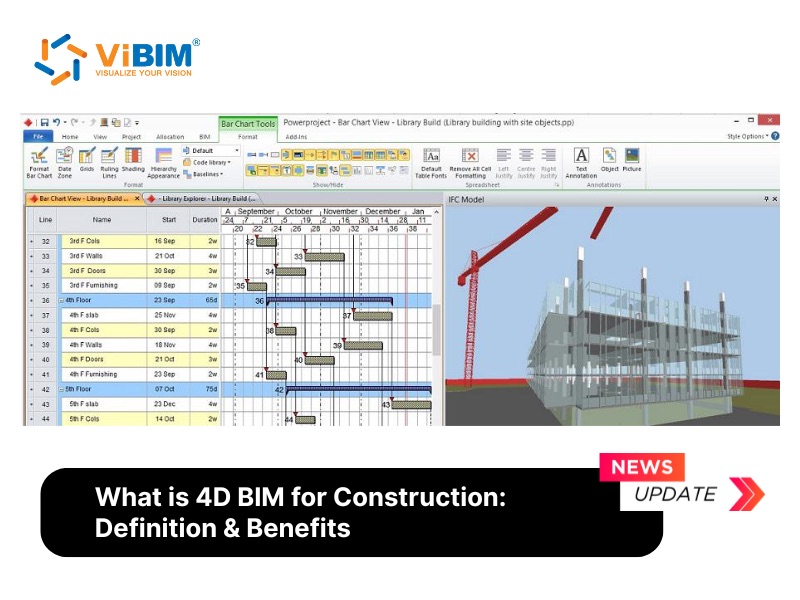
What is 4D BIM for Construction?
4D Building Information Modeling (BIM) is the process of intelligently linking a 3D model with time and schedule information. The “4D” refers to the addition of time as the fourth dimension to a 3D model’s spatial dimensions (length, width, and height). This integration creates a dynamic, data-rich virtual model of the construction process, allowing project teams to visualize the sequence of construction activities over time.
More than just an animation, 4D BIM is a powerful project management tool that provides a comprehensive, day-by-day view of how a building will be constructed. This allows stakeholders to identify potential scheduling conflicts, logistical issues, and safety hazards before they occur on-site.
Unlike a static 3D model, a 4D model simulates the entire construction process, showing how the building and site will look at any point in time.
4D BIM is used to create detailed construction simulations for:
- Planning and Scheduling: By linking model elements to a construction schedule, teams can simulate the entire construction process from start to finish.
- Progress Monitoring: The model can be updated with real-time data from the site to track progress against the plan.
- Resource Management: It allows for the proactive management of materials, equipment, and labor.
The main benefit of using 4D BIM is that it provides a clear and shared understanding of the construction plan, which helps to reduce delays, control costs, and improve the overall quality and safety of the project.
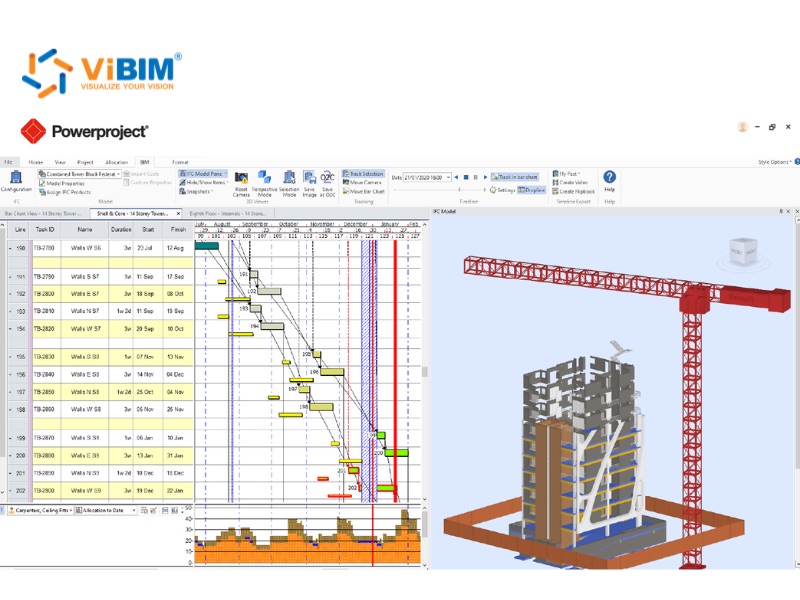
Benefits of 4D BIM for Construction
By integrating time, 4D BIM enables virtual construction rehearsals that deliver benefits such as improved planning, scheduling, and site safety while enhancing team collaboration and enabling smarter, time-based clash detection for predictable results. Here are six detailed benefits of 4D BIM for construction
Improved Construction Scheduling
4D BIM significantly enhances construction scheduling by providing a visual and dynamic representation of the project timeline. This allows for more accurate and realistic planning, as schedulers can see the direct impact of their decisions on the construction sequence. By linking the 3D model with the schedule, potential conflicts and logistical issues that might not be apparent in a traditional Gantt chart can be easily identified and resolved. This proactive approach to scheduling leads to more reliable timelines, reduced delays, and a smoother construction process.
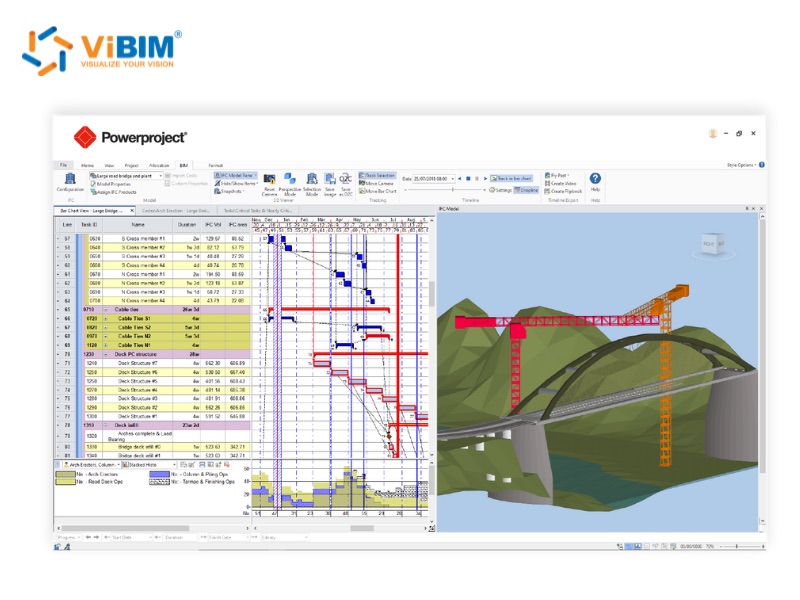
Better 4D Construction Visualization
The ability to visualize the construction process over time is one of the most powerful benefits of 4D BIM. It transforms a static set of drawings and a complex schedule into an intuitive and easy-to-understand animation of the building’s construction. This visualization is invaluable for all project stakeholders, from the owner and designers to the contractors and subcontractors. It provides a clear and shared understanding of the construction plan, helping to align expectations and facilitate more effective communication and decision-making.
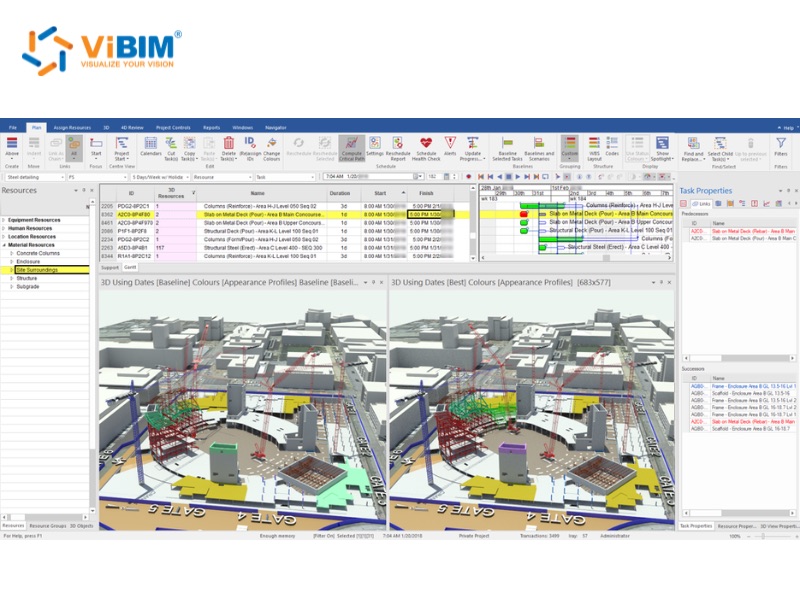
Smarter clash detection
While 3D BIM is well-known for its clash detection capabilities, 4D BIM takes it a step further by enabling time-based clash detection. This means that it can identify not only spatial conflicts between permanent building elements but also conflicts that arise over time, such as those involving temporary works, equipment, and construction activities. For example, a 4D simulation can reveal if a crane’s movement will interfere with scaffolding at a certain point in the schedule or if two trades are scheduled to work in the same space at the same time. Identifying these clashes before they occur on-site prevents costly rework and delays.
Facilitate better team collaboration and communication
4D BIM serves as a powerful collaboration and communication tool, bringing the entire project team together around a shared understanding of the construction plan. The visual nature of 4D simulations makes it easier for team members from different disciplines to communicate effectively, resolve issues, and make informed decisions. This collaborative environment fosters a sense of shared ownership and accountability, leading to a more integrated and efficient project team.
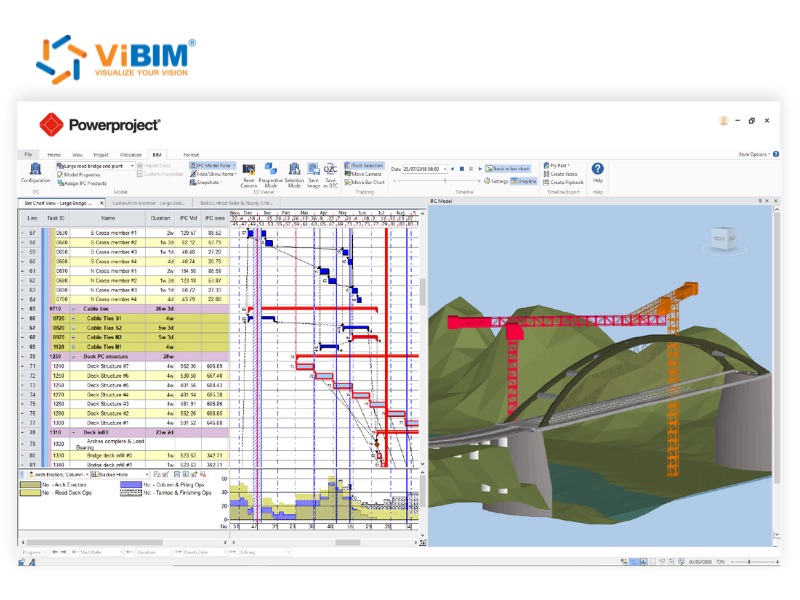
Enhanced Tracking Opportunities
By linking the 4D model with real-time data from the construction site, project managers can track progress more effectively. The model can be updated to reflect the as-built status of the project, allowing for a visual comparison of planned versus actual progress. This enhanced tracking provides greater insight into the project’s performance, enabling project managers to identify potential delays early and take corrective action to keep the project on schedule.
Construction site safety
4D BIM can significantly improve construction site safety by allowing teams to visualize and plan for potential hazards before they occur. By simulating the construction process, safety managers can identify high-risk activities and areas, and develop proactive safety plans to mitigate those risks. For example, a 4D simulation can be used to plan the logistics of material delivery and crane movements to avoid creating hazards for workers on-site. This focus on safety planning helps to create a safer working environment for everyone on the project.
Potential Risks and Challenges of Implementing 4D BIM in Construction
Despite its numerous benefits, the implementation of 4D BIM is not without its challenges. Organizations considering adopting 4D BIM should be aware of the following potential risks and challenges:
- Contractual and Legal Issues: Traditional contracts are often tailored to paper-based processes. The use of a shared digital model raises questions about data ownership, copyright, responsibility for accuracy, and liability, which require new contractual language and agreements to mitigate risk.
- Technical and Interoperability Hurdles: Effective 4D BIM relies on the seamless exchange of data between different software platforms used by architects, engineers, and contractors. Poor interoperability can lead to data loss or corruption, requiring manual rework and undermining the efficiency of the process.
- High Upfront Costs: Adopting 4D BIM involves significant investment. This includes not only the cost of software and hardware upgrades but also the substantial expense of training staff and the initial loss of productivity during the learning curve.
- Process Management and Data Integrity: Effective application of 4D BIM requires the project to be closely managed in coordination and supported by a full BIM environment throughout the construction stages. If the underlying 3D model data, schedule information, or input from any party deviates from the plan, the accuracy and reliability of the 4D simulation will be affected, potentially losing its value.
- Skill and Knowledge Gap: There is a notable skills gap in the industry. Many experienced professionals are accustomed to 2D processes, while recent graduates may lack practical construction experience. Finding or training staff who are proficient in both BIM tools and construction processes is a major challenge.
- Level of Detail (LOD): A 4D model requires a specific Level of Development. For example, a concrete slab that a designer models as a single object may need to be broken down into multiple pours to reflect the actual construction sequence, requiring additional modeling effort by the contractor.
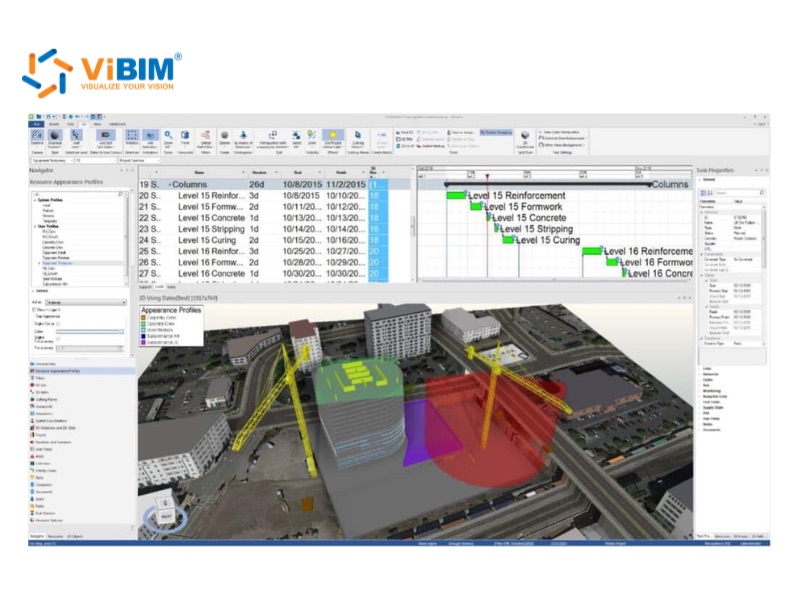
Real-world Applications of 4D BIM in Construction
4D BIM is being successfully applied in a wide range of construction projects around the world, from complex infrastructure projects to large-scale commercial and residential buildings. Some of the real-world applications of 4D BIM include:
- Complex Infrastructure Planning: In large-scale public works like the Victoria Station Upgrade, the 4D model is used for detailed sequence simulation. This allows teams to virtually rehearse high-risk construction activities within tight timeframes, such as the six-day window for building an underpass, to ensure completion with minimal disruption to public services.
- High-Rise Construction Cycle Optimization: For tall, repetitive structures like the One Island East office tower, 4D analysis is applied to validate and optimize floor-by-floor construction cycles. This simulation ensures that an aggressive, multi-day cycle for each floor is feasible and can be safely maintained throughout the project.
- Stakeholder Communication in Sensitive Environments: In renovations of active facilities like St. Joseph Hospital, the 4D model is used as a critical communication tool. It visually demonstrates the planned construction schedule to non-technical stakeholders, such as hospital staff, to coordinate activities and mitigate the impact on ongoing patient care.
- Logistics and Equipment Planning for Prefabrication: For projects utilizing modular construction, such as the NTU Student Residence Halls, 4D simulation is used to plan site logistics. This includes optimizing the location and operation of tower cranes to ensure the efficient and safe hoisting and installation of prefabricated modules.
The Future of 4D BIM in Construction
The evolution of 4D Building Information Modeling is defined by a trajectory toward deeper automation, predictive intelligence, and seamless technological integration. Future developments center on the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and generative scheduling algorithms. These systems analyze geometric models and construction constraints to automatically formulate and optimize thousands of potential project sequences, moving beyond simple visualization to true process optimization. This intelligent planning is amplified by integration with the Internet of Things (IoT) and cloud computing. IoT sensors on equipment and materials provide real-time data feeds directly into the 4D model, while cloud platforms ensure this information is universally accessible to all project stakeholders.
The ecosystem is further enriched by Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), and point cloud scanning. This synergy creates a critical feedback loop, allowing for the direct comparison of as-built conditions against the 4D plan for immediate progress verification and variance analysis. By providing this clear, data-driven view of the project, 4D BIM facilitates superior decision-making, optimizes resource allocation, and reduces material waste, directly contributing to more sustainable construction outcomes. Ongoing research and development efforts focus on refining these complex workflows and simplifying user interfaces, making advanced 4D BIM more accessible and driving its adoption as a standard practice for managing project complexity.
Explore more dimensions of BIM: From 3D to 6D BIM & Beyond
FAQs
4D BIM vs 3D BIM
The primary difference between 4D BIM and 3D BIM is the addition of the time dimension. A 3D BIM model is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building. A 4D BIM model takes this a step further by linking the 3D model with a construction schedule, allowing for the visualization of the construction process over time. While 3D BIM is excellent for visualizing the final building and for clash detection between static elements, 4D BIM provides a dynamic view of the construction sequence, enabling better planning, coordination, and risk management throughout the construction phase.
4D BIM vs 5D BIM
5D BIM adds another dimension to the model: cost. While 4D BIM integrates time and scheduling data, 5D BIM incorporates cost and financial data, allowing for real-time cost estimation and financial oversight throughout the project lifecycle. 4D BIM supports the construction process by optimizing the schedule and identifying potential logistical issues, while 5D BIM adds a layer of financial control, enabling teams to track budgets, manage costs, and make more informed financial decisions.
4D BIM represents a significant leap forward from traditional project planning. By integrating the dimension of time with a data-rich 3D model, it provides an unparalleled tool for visualizing, analyzing, and optimizing the entire construction sequence. The benefits—from improved scheduling and proactive clash detection to enhanced team collaboration and site safety—directly address the core challenges of modern construction.
As projects continue to increase in complexity and schedules become more compressed, the ability to rehearse construction virtually is no longer a luxury but a necessity. 4D BIM provides the clarity needed to mitigate risks, improve efficiency, and ensure that all stakeholders are aligned. For any organization looking to enhance predictability and performance, embracing 4D BIM is a critical step toward building a more successful and resilient future.