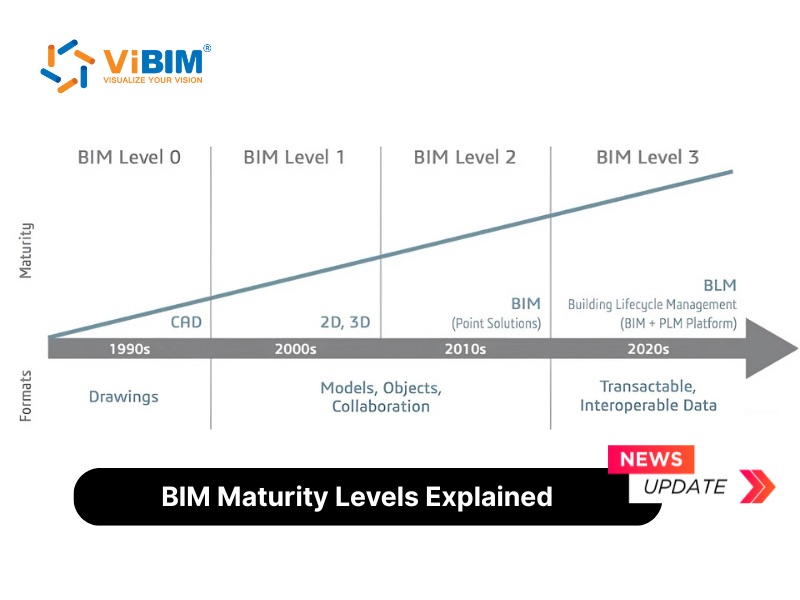
Facility management (FM) is crucial for the efficient and effective operation of buildings throughout their lifecycle. It encompasses a wide range of activities, including maintenance, space management, and asset tracking, all aimed at ensuring the building meets the needs of its occupants and owners. However, traditional facility management methods often face significant challenges. These can include fragmented information, reliance on outdated 2D drawings, and difficulties in accessing and visualizing crucial building data. Such challenges can lead to inefficiencies, increased operational costs, and a reduced ability to proactively manage building assets.
Building Information Modeling (BIM) offers a transformative approach to facility management by providing a centralized, data-rich digital representation of a building. Unlike traditional methods that often involve sifting through disparate documents and drawings, BIM integrates geometric and non-geometric data into an intelligent model. This allows facility managers to access comprehensive and accurate information quickly, leading to more informed decision-making and proactive maintenance strategies. The application of BIM in facility management bridges the gap between the design and construction phases and the operational lifecycle of a building, offering numerous benefits such as improved data accessibility, enhanced space and asset management, and streamlined work order processes. This article will explore nine major advantages of using BIM for facility management, demonstrating how this technology is revolutionizing the way buildings are operated and maintained.
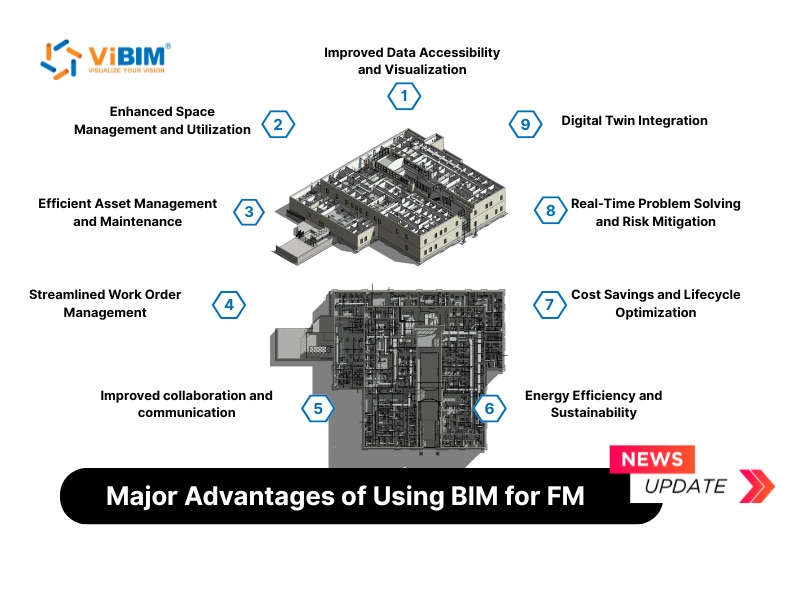
Improved Data Accessibility and Visualization
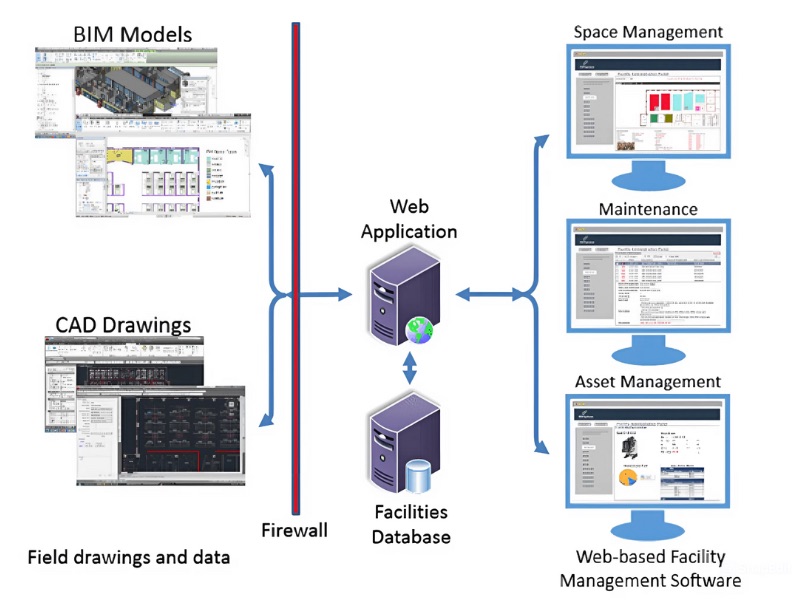
One of the primary advantages of using BIM for facility management is the significant improvement in data accessibility and visualization. BIM models serve as a central repository for all building-related information, from architectural and structural details to MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems and equipment specifications. This digital twin provides facility managers with an intuitive and interactive 3D interface to access and visualize complex building data that would traditionally be scattered across numerous 2D drawings and documents. With BIM, facility managers can easily navigate the virtual model to locate specific assets, understand their spatial relationships, and retrieve associated information such as manufacturer details, maintenance history, and performance data. This enhanced visualization capability allows for quicker identification of potential issues, better-informed decision-making, and more efficient planning of maintenance and repair activities. For example, understanding the precise location and connections of an HVAC unit within a complex ceiling space becomes straightforward with a BIM model, a task that could be time-consuming and error-prone using traditional 2D plans.
See more details about What is BIM for facility management?
Enhanced Space Management and Utilization
BIM offers powerful tools for enhanced space management and utilization throughout a building’s lifecycle. Facility managers can leverage the detailed spatial information embedded within a BIM model to optimize a building’s layout, track space allocation, and plan for future needs more effectively. The 3D visualization capabilities of BIM allow for a clear understanding of how different spaces are being used and how they interact with each other. This is particularly beneficial for complex facilities like hospitals or corporate offices where efficient space utilization is critical. BIM models can be used to conduct spatial analyses, identify underutilized areas, and plan reconfigurations with greater accuracy and less disruption. Furthermore, BIM facilitates accurate area calculations and tracking of departmental space assignments, which is crucial for internal cost allocation and strategic planning. The ability to link space data with occupancy information and asset locations within the BIM model provides facility managers with a holistic view of their building’s resources, enabling them to make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency and user comfort.
Source: BIM-FM Consortium-BIM-Guide-v2_1.pdf
Efficient Asset Management and Maintenance
BIM significantly improves the efficiency of asset management and maintenance by providing a centralized and easily accessible database of all building components and equipment. Each asset within the BIM model can be linked to a wealth of information, including manufacturer specifications, installation dates, warranty details, maintenance schedules, and repair histories. This allows facility managers to quickly retrieve crucial data for any asset, streamlining troubleshooting and repair processes. For instance, if a piece of equipment malfunctions, the FM team can access its BIM object to understand its location, specifications, and maintenance history, leading to faster diagnosis and resolution. Proactive maintenance strategies can be developed by integrating maintenance schedules directly into the BIM model, triggering alerts for upcoming servicing requirements. This shift from reactive to preventative maintenance helps to extend asset lifespan, reduce downtime, and minimize unexpected repair costs. Furthermore, the ability to visualize assets in their 3D context aids in planning maintenance tasks, ensuring that technicians have the necessary access and information before starting work.
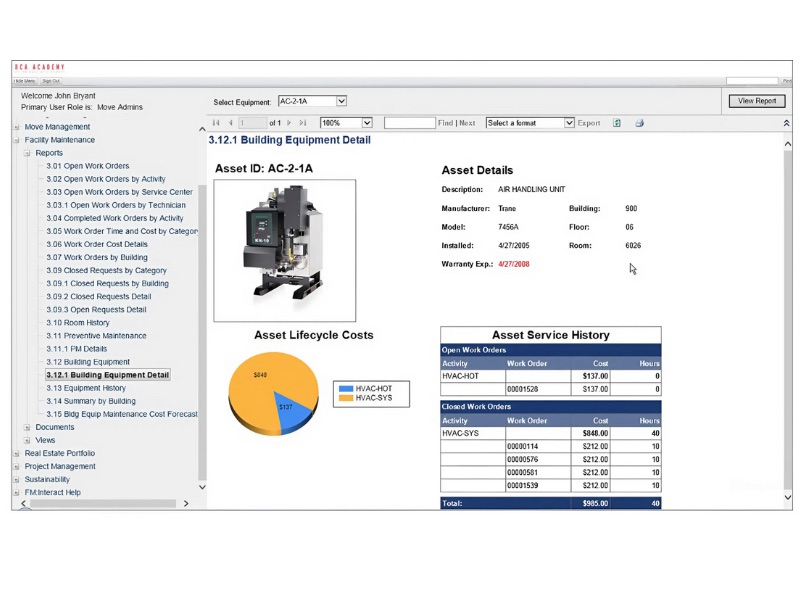
Source: BIM-FM Consortium-BIM-Guide-v2_1.pdf
Streamlined Work Order Management
Integrating BIM with Computerized Maintenance Management Systems (CMMS) streamlines the entire work order management process. When a maintenance issue arises, a work order can be generated and directly linked to the specific asset or location within the BIM model. This provides technicians with precise visual information about the problem’s location and the affected asset, eliminating the guesswork often associated with paper-based work orders and 2D drawings. Facility staff can access the BIM model on mobile devices in the field, view the relevant asset information, and update the work order status in real-time. This digital workflow improves communication between the FM team and technicians, reduces the time spent locating assets and understanding the scope of work, and ensures that maintenance activities are accurately tracked and documented. The ability to visualize the impact of a shutdown on interconnected systems within the BIM model also aids in planning work orders to minimize disruption to building occupants.
Improved collaboration and communication
BIM fosters improved collaboration and communication among all stakeholders involved in facility management, including building owners, facility managers, maintenance staff, and external contractors. The shared, data-rich 3D model acts as a common language, ensuring everyone has access to the same accurate and up-to-date building information. This reduces misunderstandings and misinterpretations that can arise from relying on outdated or inconsistent 2D documentation. Coordination meetings become more effective when using BIM, as stakeholders can visualize issues within the 3D model, facilitating quicker problem-solving and decision-making. For instance, when planning a renovation or equipment replacement, the BIM model can be used to clearly communicate the proposed changes and their potential impacts on existing systems to all involved parties. This collaborative environment leads to more efficient workflows, reduced errors, and ultimately, better-managed facilities.

Source: BIM-FM Consortium-BIM-Guide-v2_1.pdf
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
BIM plays a crucial role in enhancing energy efficiency and promoting sustainability in facility management. By integrating energy analysis tools with the BIM model, facility managers can simulate and evaluate the building’s energy performance under various conditions. This allows for the identification of energy-intensive areas and equipment, and the development of strategies to optimize energy consumption. For example, sensor data from building automation systems can be linked to the BIM model to provide real-time monitoring of energy usage, helping to pinpoint inefficiencies and inform operational adjustments. Furthermore, when planning upgrades or retrofits, BIM enables the evaluation of different design options and material choices for their impact on energy performance and sustainability goals, such as LEED certification. The ability to accurately model and analyze factors like daylighting, thermal performance, and HVAC system efficiency within BIM empowers facility managers to make informed decisions that reduce environmental impact and lower operational costs.
Cost Savings and Lifecycle Optimization
The adoption of BIM for facility management leads to significant cost savings and optimizes the lifecycle performance of a building. By improving data accuracy and accessibility, BIM reduces the likelihood of errors and rework during maintenance and renovation projects, directly cutting down on associated costs. Proactive maintenance scheduling, facilitated by BIM-CMMS integration, minimizes unexpected equipment failures and costly emergency repairs. Efficient space management and utilization, as discussed earlier, also contribute to cost savings by ensuring that building space is used optimally, potentially reducing the need for additional leased space. Over the building’s lifecycle, the ability to accurately track asset performance and maintenance costs within the BIM environment allows for better long-term capital planning and budgeting for replacements and upgrades. Furthermore, the energy efficiencies gained through BIM-informed strategies translate directly into reduced utility expenses.
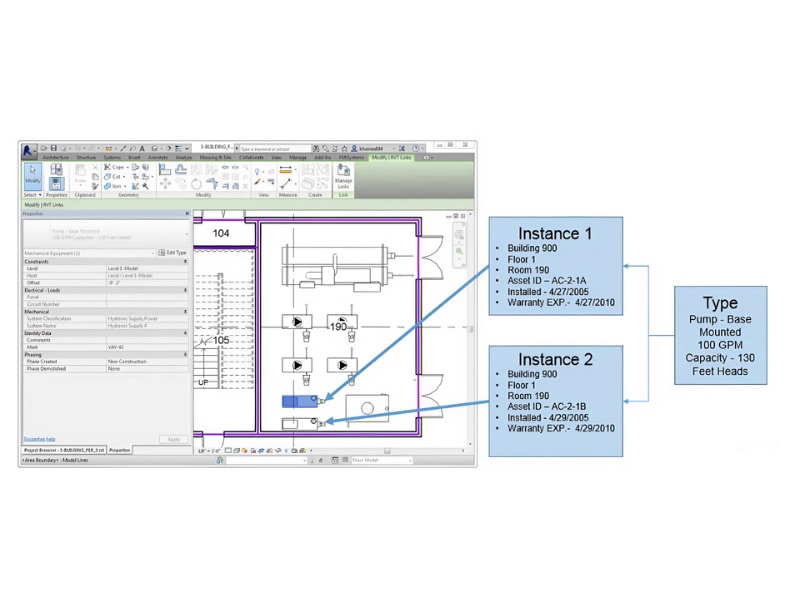
Source: BIM-FM Consortium-BIM-Guide-v2_1.pdf
Real-Time Problem Solving and Risk Mitigation
Access to a comprehensive digital twin of the facility allows for faster and more effective real-time problem-solving. When an issue occurs, such as an equipment failure or a leak, facility managers can quickly consult the BIM model to understand the affected systems, their interdependencies, and the potential impact on operations. This enables a more rapid and targeted response, minimizing downtime and mitigating potential risks. For example, in the event of a security concern, the BIM model can provide immediate information about access routes, security systems, and critical infrastructure.
Digital Twin Integration
The concept of a Digital Twin is a powerful extension of BIM for facility management. A Digital Twin is a dynamic virtual representation of a physical asset, which is continuously updated with real-time data from sensors and operational systems. By integrating the BIM model with IoT (Internet of Things) devices and building automation systems, facility managers can create a live, interactive Digital Twin of their building. This allows for real-time monitoring of building performance, including energy consumption, equipment status, and environmental conditions. Facility managers can use the Digital Twin to analyze operational data, identify trends, predict potential failures, and optimize building systems for efficiency and occupant comfort. For example, sensor data indicating an unusual vibration pattern in an HVAC unit could trigger an alert within the Digital Twin, allowing maintenance teams to investigate and address the issue before a major breakdown occurs. The Digital Twin also facilitates “what-if” scenario planning, enabling facility managers to simulate the impact of operational changes or system adjustments before implementing them in the physical building.

In conclusion, adopting BIM for facility management offers a multitude of advantages that translate into more efficient, cost-effective, and sustainable building operations. From improved data accessibility and enhanced space management to streamlined maintenance and real-time problem-solving, BIM empowers facility managers with the tools and information needed to optimize building performance throughout its entire lifecycle. As BIM technology continues to evolve, its integration with other smart building technologies like digital twins and IoT will further revolutionize the way facilities are managed, delivering even greater value to building owners and occupants.
ViBIM specializes in providing comprehensive facility management BIM models services, delivering facility managers with accurate digital representations of their physical assets.