Civil engineering is the discipline that focuses on the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. This vast field covers various specialties, including structural, transportation, and environmental engineering.
BIM in civil engineering refers to the use of digital tools and software to generate a 3D model that incorporates all aspects of a construction project, including architecture, structure, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, and Plumbing) systems. Through these models, engineers can visualize project outcomes, detect clashes, and optimize construction processes. BIM also enhances coordination among architects, structural engineers, and contractors, reducing design errors, minimizing delays, and improving overall project efficiency.
This article from ViBIM will explore how BIM is transforming civil engineering, detailing its benefits, applications, and the improvements it brings to every stage of construction, from planning to execution.
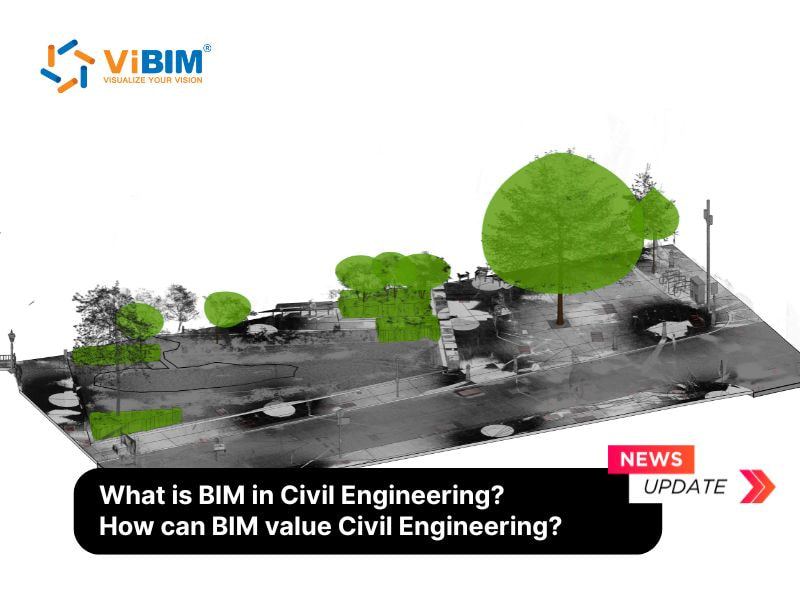
What is civil engineering?
Civil engineering encompasses the design, construction, and maintenance of infrastructure, including roads, bridges, and buildings. This industry applies scientific principles to create and maintain public and private works, with specialties in areas like structural, transportation, and environmental engineering. Civil engineers tackle infrastructure challenges, focusing on sustainability, and require skills in mathematics, physics, and project management.
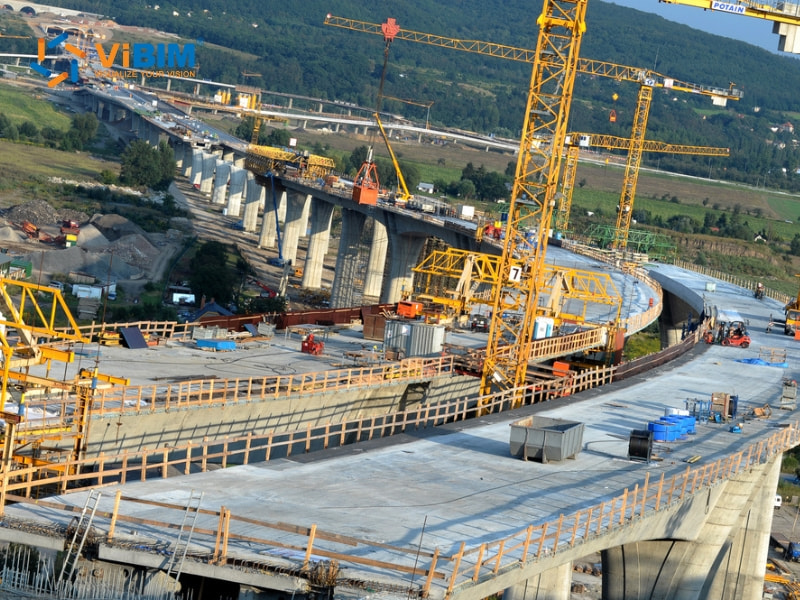

Importance of BIM in civil engineering
BIM in civil engineering refers to the use of digital technologies to create detailed 3D models that represent all components of a construction project. This includes architectural, structural, and MEP (Mechanical, Electrical, Plumbing) elements, allowing for better visualization, analysis, and planning. It enables a seamless exchange of information among project teams throughout the design, construction, and maintenance stages, often utilizing openBIM protocols to facilitate unrestricted data sharing across different software platforms.
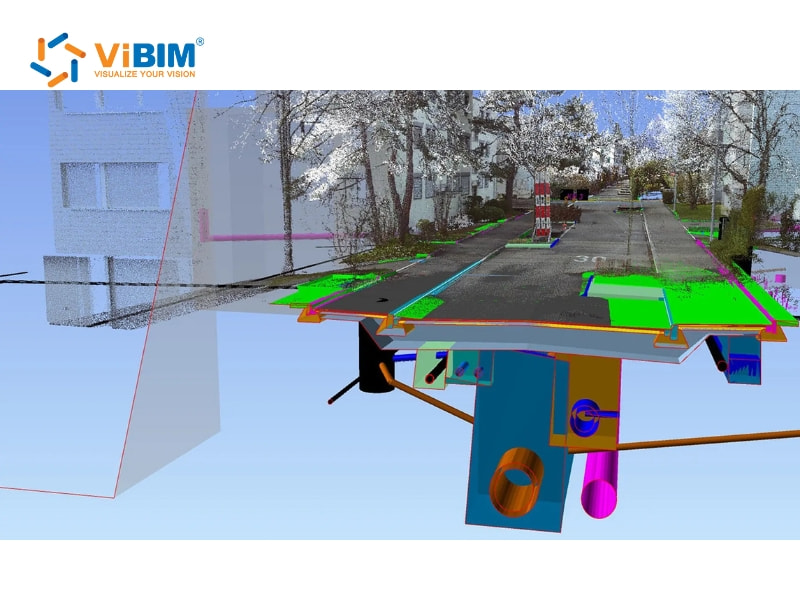
With BIM, civil engineers can create data-rich 3D models of structures, such as bridges, roads, and tunnels, that simulate their performance under real-world conditions. This helps them detect potential clashes, design flaws, or weak points early in the design phase, preventing costly rework later on.
Engineers also utilize BIM to streamline BIM coordination with other disciplines, manage on-site workflows, and track construction progress in real-time. Beyond the build phase, BIM models support maintenance and future upgrades, giving civil engineers a reliable digital asset throughout the project’s lifecycle.
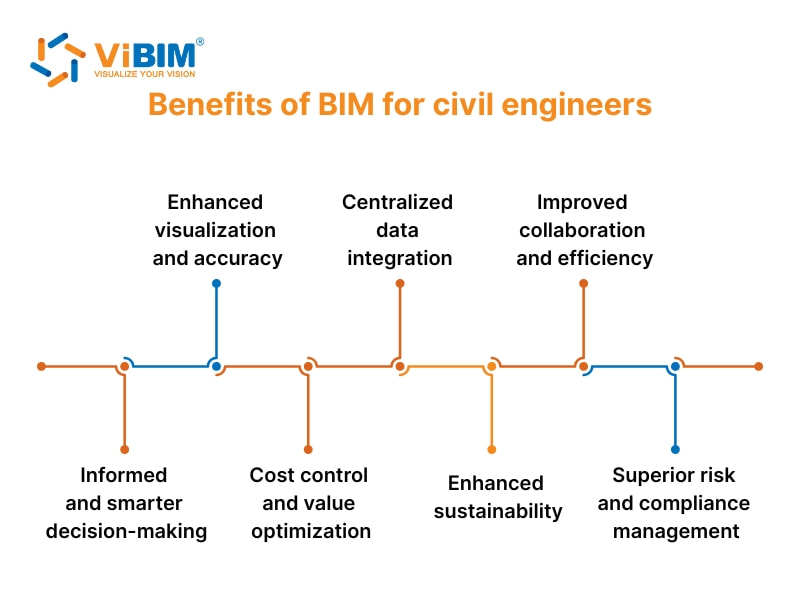
Benefits of BIM for civil engineers
BIM offers seven key benefits that significantly enhance the efficiency and accuracy of civil engineering projects. These advantages streamline workflows, reduce risks, and ensure better project outcomes.
- Enhanced visualization and accuracy: BIM allows civil engineers to visualize projects with detailed 3D models, clash detection, and simulations, improving design validation and precision in material estimates, costs, and timelines.
- Centralized data integration: BIM integrates diverse data sources, such as materials, schedules, and costs, into a unified model, minimizing errors and enabling better collaboration among all project stakeholders with consistent, up-to-date information.
- Improved collaboration and efficiency: BIM promotes real-time data sharing and updates, helping teams across disciplines to collaborate effectively, identify potential issues early, and avoid costly rework or delays.
- Informed and smarter decision-making: BIM provides civil engineers with detailed insights into construction sequences through 4D BIM, resource allocation, and site conditions, enabling better decision-making to optimize project safety and performance.
- Cost control and value optimization: BIM’s accurate quantity take off data and material estimations enable precise budgeting and resource allocation, helping to control costs and maximize project value throughout its lifecycle.
- Enhanced sustainability: BIM supports sustainable design by allowing engineers to simulate energy efficiency, material usage, and environmental impact early on, helping to create eco-friendly, energy-efficient infrastructure.
- Superior risk and compliance management: BIM enables civil engineers to anticipate and mitigate risks, plan safety measures, and ensure compliance with building codes and regulations, reducing both legal and operational risks.
What are the BIM use cases in civil engineering?
BIM has a wide range of applications in civil engineering, making it a valuable tool for infrastructure projects of all scales. It is utilized in various domains to improve efficiency, safety, and long-term planning.
- Infrastructure Development: BIM supports the design and management of infrastructure projects, including highways, bridges, tunnels, and railways. Engineers utilize 3D models to analyze ground conditions, traffic flow, and construction materials, enabling them to plan more durable and cost-effective structures.
- Structural Engineering: BIM provides civil and structural engineers with precise modeling tools for analyzing stress, load, and resistance in different structures. Engineers can simulate external forces, adjust design parameters, and confirm stability before construction begins, thereby reducing the likelihood of failures.
- Urban Planning and Smart Cities: BIM enables city planners to create intelligent 3D urban layouts that integrate data on population, transportation, and environmental impact. These models help plan sustainable neighborhoods and improve infrastructure connections, supporting the vision of more livable and efficient cities.
- Water Management and Utilities: BIM enables the design of effective water systems, drainage networks, and treatment facilities. Engineers can predict water flow behavior, detect leaks or blockages, and refine system layouts to enhance reliability and reduce environmental risks.
- Construction Site Management: BIM integrates on-site management tools that connect project teams with real-time data. Managers can track progress, control materials, and monitor worker safety through sensors or drones, making project execution smoother and more transparent.
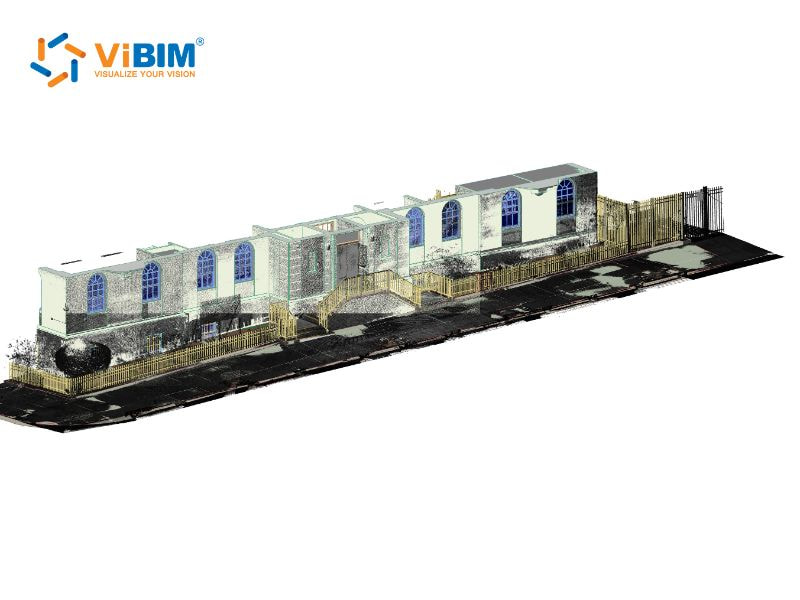

Advanced BIM-driven technologies in civil engineering
There are four modern technologies that works in conjunction with BIM to support safer and more accurate civil engineering activities, and this combination provides teams with stronger control over data, progress tracking, and field coordination.
- Robotics in BIM: Robots guided by BIM data support masonry work, drilling tasks, and layout marking, thereby improving precision while reducing manual effort and safety risks through consistent movement and automated reporting.
- Positioning and navigation: Spatial datasets within BIM models guide drones and field robots, providing support for location tracking, obstacle detection, and route planning in areas with weak GPS signals, thereby maintaining steady and safe site operations.
- VR and AR tools: Immersive VR environments support design reviews and safety training, while AR layers projected on-site help teams compare planned layouts with real-world conditions, reducing mismatched work and communication issues.
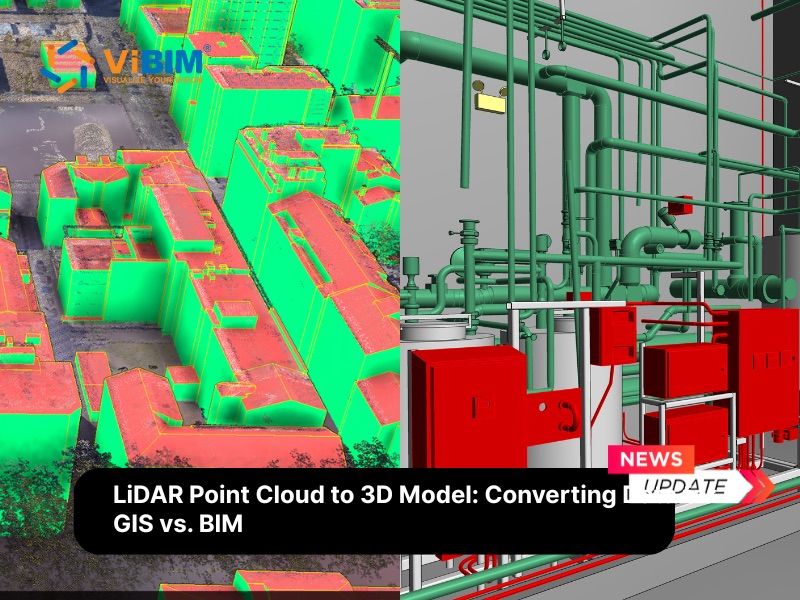
- Scan to BIM workflows: Point cloud data captured by terrestrial or mobile LiDAR supports accurate digital reconstruction of bridges, tunnels, and existing structures; this often involves precise point cloud registration and effectively utilizing Topography Scan to BIM Services to reduce measurement errors while improving planning for repairs and upgrades.
Essential BIM software for civil engineers
Here are seven essential BIM software tools for civil engineers that play a pivotal role in modernizing the design and construction process:
- Revit: Revit is a comprehensive BIM software that allows all stakeholders to collaborate on a project simultaneously. Its parametric modeling and visualization capabilities help streamline design changes and improve project efficiency.
- Civil 3D: Civil 3D is a specialized tool for civil engineering that supports the design of roads, highways, and drainage systems. It offers 3D modeling, analysis, and robust documentation features, making it indispensable for civil engineers.
- Tekla Structures: Tekla Structures is a powerful BIM software for structural engineering, particularly for concrete and steel structures. It provides advanced detailing, clash detection, and material identification, making it ideal for complex projects like bridges and tunnels.
- Bentley Systems: Bentley Systems offers several BIM solutions tailored for civil engineering. Key software includes MicroStation for CAD, OpenRoads Designer for road design, and ProjectWise for project collaboration and document management.
- ArchiCAD: ArchiCAD, developed by Graphisoft, is a widely used BIM tool that excels in 3D modeling for civil engineering projects. Its versatile tools help engineers design, visualize, document, and manage projects effectively from start to finish.

This article has explored BIM in civil engineering by examining its key concepts, use cases, and the tools that empower civil engineers to improve the design and construction process. The integration of BIM into civil engineering helps optimize workflows, enhances collaboration, and improves project accuracy, allowing engineers to make better-informed decisions and deliver projects more efficiently. By implementing BIM, civil engineers can ensure higher precision, better cost control, and greater sustainability.
For professionals seeking to leverage BIM in civil engineering, ViBIM offers specialized Scan to BIM services and Revit 3D BIM modeling services, particularly focusing on Point Cloud data to create accurate 3D models. With expertise in Revit and the Autodesk platforms, ViBIM is a reliable partner for building surveyors, as-built modeling, and engineering projects.
Contact ViBIM today to discuss your requirements and receive a complimentary quote.
Vietnam BIM Consultancy and Technology Application Company Limited (ViBIM)
- Address: 10th floor, CIT Building, No 6, Alley 15, Duy Tan street, Cau Giay ward, Hanoi, Vietnam
- Phone: +84 944 798 298
- Email: info@vibim.com.vn